Abstract: 5585
Session: Inflammatory Modulation in Sarcoidosis, Lung Transplant, and Other Diseases
Poster available: Tuesday May 17, 2022 9:30 AM - 3:45 PM
Xentria presents new data on XTMAB-16 with a poster presentation at the ATS International Conference 2022. Xentria partnered with Dr. Elliott Crouser, M.D., Professor of Pulmonology, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine at The Ohio State University to explore the potential for XTMAB-16 to reduce immune cell-induced inflammation.
Key findings from the data include:
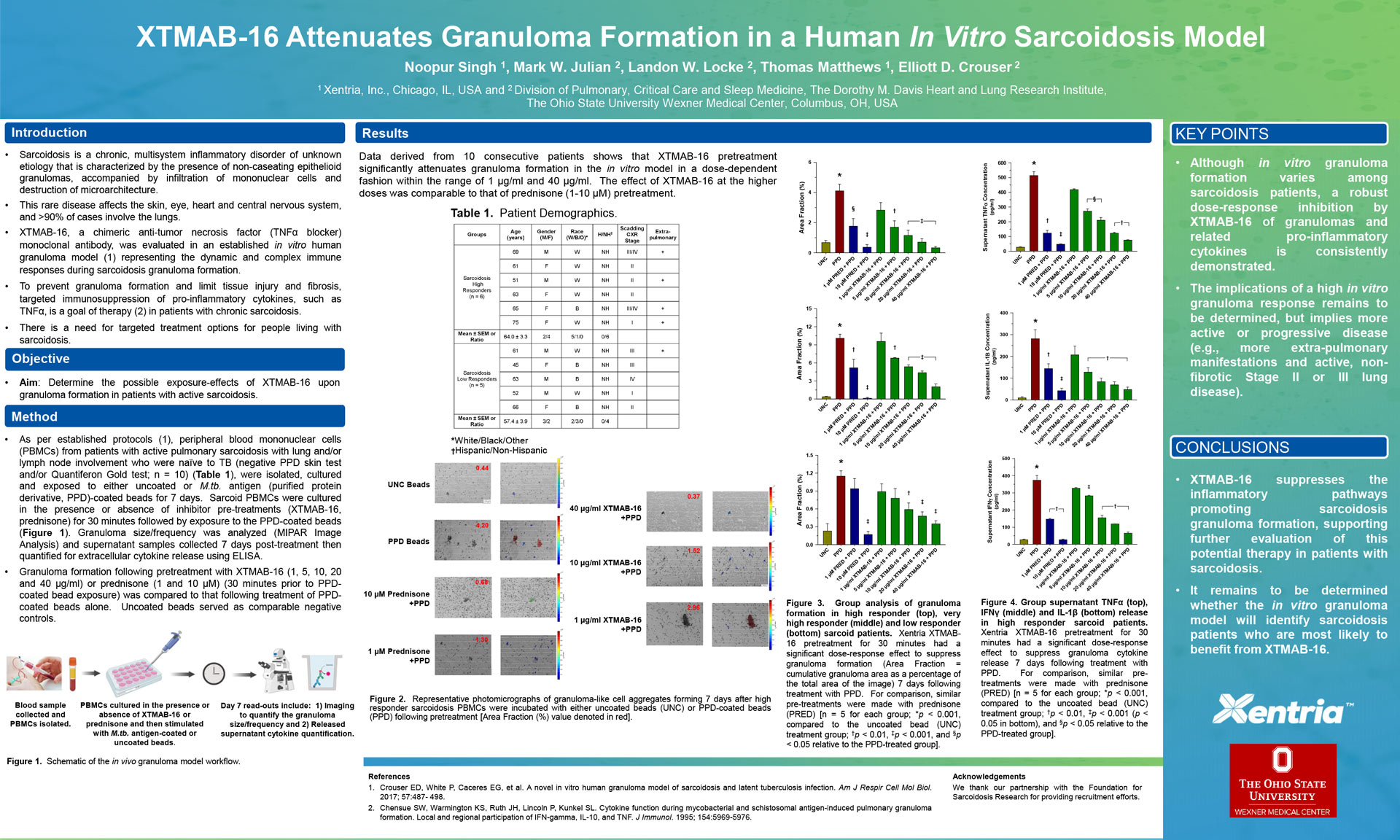
- Data derived from ten consecutive patients showed that pretreatment with XTMAB-16 significantly, and dose-dependently, reduces granuloma formation in an in vitro model within the range of 1 μg/ml and 40 μg/ml.
- XTMAB-16 consistently inhibited in vitro granuloma formation (the key inflammatory feature of sarcoidosis) and related inflammatory molecules, based on an established laboratory model using the actual immune cells of sarcoidosis patients.
- XTMAB-16 was comparable to the currently accepted first line treatment, corticosteroids, for suppression of in vitro sarcoidosis granuloma formation. The efficacy of XTMAB-16 for reducing disease activity in humans remains to be determined in clinical trials.
About XTMAB-16
XTMAB-16 is novel biologic developed by Xentria to address the unmet medical need for patients with sarcoidosis, a rare inflammatory disease that affects multiple organs in the body. XTMAB-16 is a monoclonal antibody designed to suppresses the inflammatory pathways promotion of sarcoidosis granuloma formation. No TNF-α inhibitor is currently approved for the treatment of sarcoidosis.
About Xentria
Sarcoidosis is a chronic, multisystem inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology that is characterized by the presence of noncaseating epithelioid granulomas, accompanied by infiltration of mononuclear cells and destruction of microarchitecture. The disease can affect the skin, eyes, heart, and central nervous system, and >90% of cases involve the lungs. While medications for systemic organ involvement often control this disease, some patients fail to respond to initial treatments and require additional targeted therapy, resulting in significant costs and treatment burdens. This disease presents a significant unmet medical need and a very important area of research and development for Xentria.



American Thoracic Society (ATS)
International Conference 2022
Date: May 13-18, 2022
Location: San Francisco
Presentation: Abstract poster